Test Modules
All test development and execution in Action Based Testing is based on test modules.
Test modules
The test module is the work file in which you create tests. Its essence is to contain a group of test cases with a similar, and if possible narrowly-defined, scope. A TestArchitect project is typically comprised of multiple test modules, which are often grouped into folders and subfolders of the project. Test modules should be designed to run independently from each other, while the test cases within a test module can have dependencies among themselves.
An essential success factor in Action Based Testing Action Based Testing is to divide your tests into well-differentiated and well-defined test modules. Within a test module, all actions, especially the family of check actions, should directly relate to the defined scope of the test module. This way it is easy to keep abreast of large tests, and functional changes to a system under test need only have a localized effect on the test suite - that is, only the relevant test modules are affected.
The test module contains objectives and test cases. The objectives are an auxiliary device to further refine the scope of the test module. They allow a reader to understand why test cases are designed the way they are, and give an auditor a quick insight into the correctness and, more importantly, completeness of a test.
Care should be taken to design test modules well. They should be readable for outsiders with relatively little knowledge of technology or of details that are not needed to understand a test. Details that are needed to execute the test (like which menu item to choose to open a dialog box) should not be visible in a test module unless they are important to the scope of that test module. The details should rather be dealt with by the actions, which also means they are maintained in one place.
The test module template
Upon creation, TestArchitect populates the test module with headings for a recommended template:
The TEST MODULE heading: As a documentary line, this heading is fixed at row 1, and is the only non-optional, non-deletable heading in a test module.
The OBJECTIVES heading: The OBJECTIVES section holds every objective that is associated with the test cases. The objectives listed in it define the scope of the test module. They allow readers to understand why test cases are designed the way they are, and give an auditor a quick insight into the correctness and, more importantly, completeness of a test.
Notes:Only the test objective built-in action is allowed to appear in the OBJECTIVE section. Otherwise, the following error dialog box appears.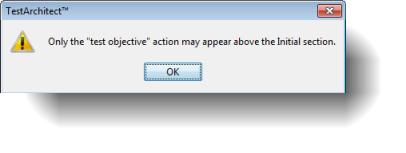
The INITIAL heading: The
INITIALsection of a test module is useful for holding action lines that are required for initialization of the test, especially when such initialization is required for all or most of the test cases in the module. For example, lines for launching the application under test, initializing it, etc., would typically appear here.A TEST CASE heading. This is a representative heading, accompanied by a representative test objective line, both of which are presented as a reminder of their utility. Typically, your test might have multiple test cases, each of which may have one or more test objectives associated with it.
Notes:Before entering the test objectives of a test case under the TEST CASE heading, you must document all test objectives of your test under the OBJECTIVES heading. Otherwise, the below error dialog box appears.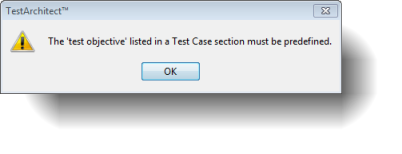
A FINAL heading. Any warranted cleanup operations upon test completion, such as closing the application under test, would typically appear here.
A typical test module should resemble the following: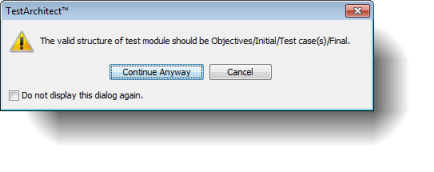
Of the above, INITIAL, FINAL, TEST CASE, and TEST OBJECTIVE are all built-in actions. They are not, however, executed at run time. Instead, they serve two purposes:
- First, they serve a documentary and organizational function. This is especially true of TEST CASE and TEST OBJECTIVE, which specify the roles of sections of your action lines in the context of an overall test plan.
- Second, the INITIAL, FINAL, and TEST CASE actions serve as entry points for execution. At the start of your execution run, you may specify exactly which of these sections of action lines are to be included in the run.
If you do not follow the recommended test module template, as discussed above, a warning dialog box appears when you save your test module. You may ignore the warning dialog box by clicking the Continue Anyway button.
Related concepts
