attach file
Description
Attach given file(s) to a web service.
Arguments
path
Path to the location of the attached file.
control name
Value of the name attribute in the HTML input tag. (See Notes.)
file name
(Optional) Attach the given file with a new name.
mime type
(Optional) MIME type of the attached file.
charset
(Optional) The character set (character encoding) to use.
Standard charset values:
US-ASCII or ISO646-US
Seven-bit ASCII, a.k.a. the Basic Latin block of the Unicode character set
ISO-8859-1
ISO Latin Alphabet No. 1, a.k.a. ISO-LATIN-1
UTF-8
Eight-bit UCS Transformation Format
UTF-16BE
Sixteen-bit UCS Transformation Format, big-endian byte order
UTF-16LE
Sixteen-bit UCS Transformation Format, little-endian byte order
UTF-16
Sixteen-bit UCS Transformation Format, byte order identified by an optional byte-order mark
Valid contexts
This action may be used within the following project items: test modules and user-defined actions.
Notes
- It is required that this built-in action must be declared before using the send http request action. When this built-in action is called, the multipart form data technique, provided by Rest Assured, is applied.
- To attach multiple files, in test procedures, call multiple attach file in sequence.
- control name:
- When a single file is attached, the value is optional. When this argument is empty, by default, the attach file action will assume a control name called file (learn more). Specifically, in HTML the control name is the attribute name of the input tag.
- To attach multiple files simultaneously, this argument is required. You must input a unique control name defined for each file attached.
- Please also note that, depending on the API-under-test, the value and availability of this argument might vary. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you read API documentations carefully. (See “Uploading Files With Real World Examples” below.)
- file name:
- When this value is empty, the default name for the attached file is file.
- Please also note that, depending on the API-under-test, the value and availability of this argument might vary. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you read API documentations carefully. (See “Uploading Files With Real World Examples” below.)
- On Windows: In order to specify mapping network drives, please disable User Account Control (UAC).
- On Linux, macOS: Mounted drives are supported.
- mime type:
- For a full list of available MIME types, refer to this site.
- When no MIME is provided, this argument is ignored during test automation.
- Please also note that, depending on the API-under-test, the value and availability of this argument might vary. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you read API documentations carefully. (See “Uploading Files With Real World Examples” below.)
- charset: Besides the standard charsets above, you can also manually enter other encoding sets. (Learn more.)
Applicable Built-In Settings
The following settings are applicable to this action: remove double quotes from cells.
Uploading Files With Real World Examples
- API-under-test: Image Upload
- control name argument:
- Required
- Input value: image
- Action lines:

- API-under-test: Image Upload
- control name argument:
- Required
- Input value: image
- file name: Required
- Action lines:
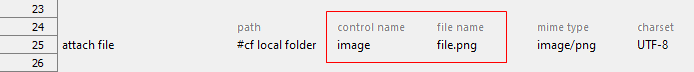
- API-under-test: Multipart Upload
- mime type argument: When this argument is empty, the default value, applied by Google Drive, is application/x-zip
- Action lines:
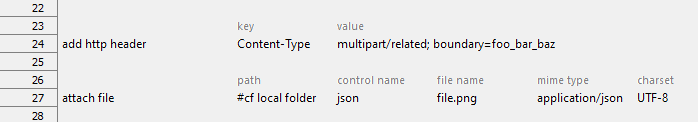
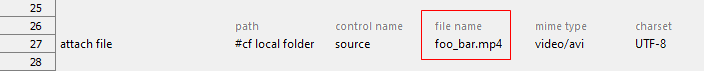
- API-under-test: Video Upload
- file name argument: Required
- Action lines:
Example
Suppose that you’d like to attach a file with the following information:
- Path to the location of the attached file: /Users/test/Desktop/TestData/Web Services/testfile.png
- Value of the name attribute in the HTML input tag: file
- Attach the given file with a new name: file.png
- MIME type of the attached file: image/png
- The character set (character encoding) to use: UTF-8
Verify the if the HTTP status of the response is 201, which means the request has been fulfilled and resulted in a new resource being created.
Action Lines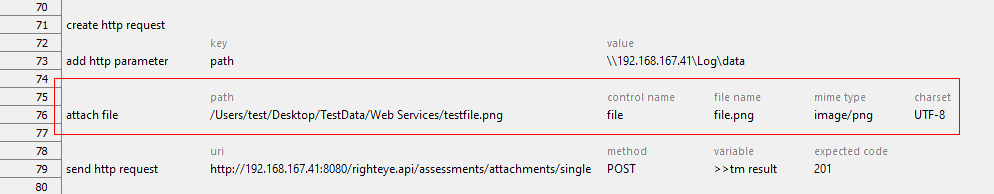
Related concepts
