execute command
Description
Execute a command-line command and return its output.
Arguments
command
Command to be executed
variable
Variable to receive the command output
timeout
(Optional) Maximum wait time for the specified command to complete execution (units: seconds; valid range: 1 to 86400; default = 300)
If the timeout is reached, the running command is terminated.
charset
(Optional) The encoding type of execute command’s output.
- Allowable values:
- Shift-JIS: Encode the file using Shift-JIS format. Recommend for use with Japanese.
- UTF-8: (Default) Encode the file using UTF-8 format.
- Allowable values:
Valid contexts
This action may be used within the following project items: test modules and user-defined actions.
Notes
This built-in action is supported only on Windows test controllers; it is effective on Windows, iOS and Android test platforms.
The execute command action can be invoked to execute any of the following:
- Command line utilities.
- Any application that can be invoked from the command line.
- An Android Debug Bridge (adb) command line that allows you to communicate with either an emulator instance or a connected Android device.
- Command lines that lets you communicate with a connected iOS device.
execute command works synchronously: that is, it causes test execution to wait for the specified command to finish before control is returned to the test. To execute commands asynchronously – that is, launch a command or application and continue with the test run without waiting – precede the contents of your command with the start command (see Example - Case 2).
ヒント:You can view the full syntax of the start command by typing start /? in the command prompt window.If you want to write the command output to a file, rather than to the variable defined in the variable argument, use the redirect command output (>) operator in your command string. For example, to redirect a directory listing to the file dirlist.txt:
command variable execute command dir > dirlist.txt x(Note that the output is fully directed to the file, and that the variable, while still a required argument, remains empty, or at its previous value.)
This action supports the <ignore> modifier. If the string
<ignore>is present as the value of any of the arguments, or any argument contains an expression that evaluates to<ignore>, the action is skipped during execution.
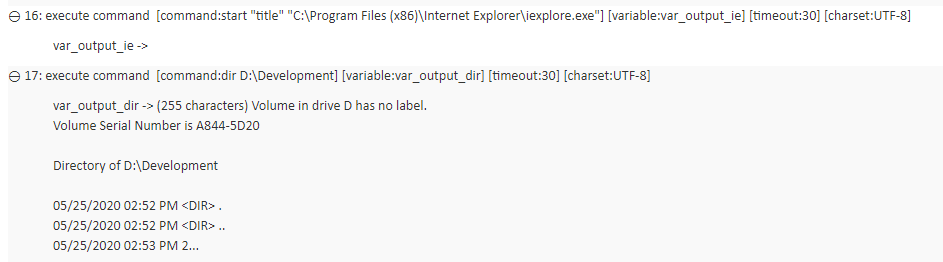
Example - Case 1
Suppose you issue the dir command in your automation script to see the available files and directories in the D:\Development directory.
Action Lines
Result
Instead of writing the dir output to the var_output variable, you can write the output to a file by using the redirect command output (>) operator.
Action Lines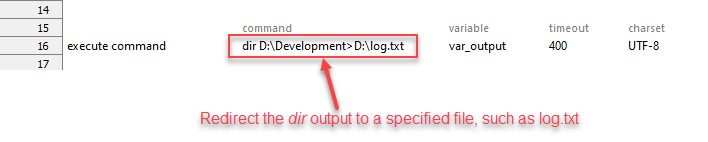
Result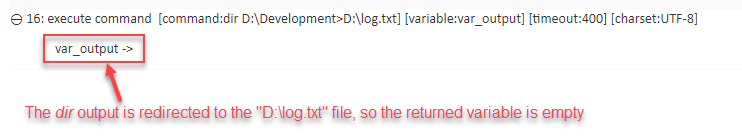
Effect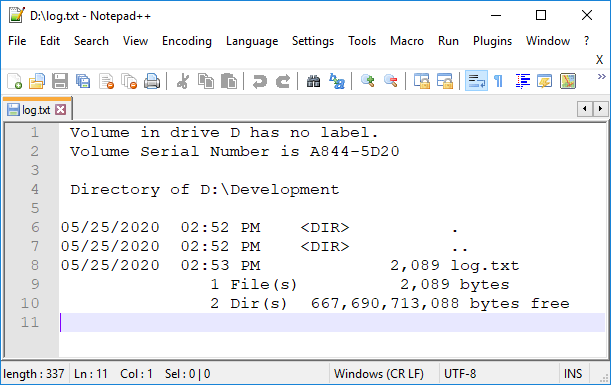
Example - Case 2
Suppose you may want to issue two commands in your automation script.
- One command is to launch an application, such as Internet Explorer, and
- the other is to see available files in a specified directory, such as D:\Development.
Additionally, these two commands must run asynchronously (without waiting for each command to finish).
Test Lines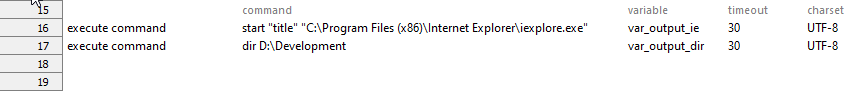
Result