configure web service settings
| Name | Description | Type | Modifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| values | Send JSON string request to a web service in order to apply new configuration settings. Important: Basic JSON syntax as required for creating profiles is as follows:
| String | None |
Example: Proxy configurations
Case 1: User-defined proxy configurations:
Suppose that you'd like add the following proxy configurations:
- Hostname:
192.168.167.29 - Port:
8888 - Protocol:
http - Proxy authentications:
- Username:
john - Password:
doe
- Username:
Your JSON string should resemble as follows:
{"proxy":{"hostname":"192.168.167.29","port":8888,"scheme":"http","username":"john","password":"doe"}}
values
configure web service settings {"proxy":{"hostname":"192.168.167.29","port":8888,"scheme":"http","username":"john","password":"doe"}}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header content-type application/json
add http header Authorization application/json
 
content
add http body #body value authenticate
 
uri method variable
send http request #api authenticate righteyes POST #"_response"&" "& ds number
Case 2: System proxy configurations:
Suppose that you'd like to apply system proxy configurations for hostname and port:
- Hostname:
system - Port:
systen - Protocol:
http - Proxy authentications:
- Username:
john - Password:
doe
- Username:
Your JSON string should resemble as follows:
{"proxy":{"hostname":"system","port":"system","scheme":"http","username":"john","password":"doe"}}
values
configure web service settings {"proxy":{"hostname":"system","port":"system","scheme":"http","username":"john","password":"doe"}}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header content-type application/json
add http header Authorization application/json
 
content
add http body #body value authenticate
 
uri method variable
send http request #api authenticate righteyes POST #"_response"&" "& ds number
Example: SSL configuration
Case 1: No SSL validation
For example, you run into a problem, because the server is using an invalid SSL certificate. The easiest way to workaround this is that you trust all hosts.
Your JSON string should resemble as follows:
{"ssl":"skip"}
values
configure web service settings {"ssl":"skip"}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header content-type application/json
add http header Authorization # tm token
 
uri method variable
send http request # api test https GET _response_TC_02
 
response status
parse http reponse #_response_TC_02 tm status_TC_02
 
text fragment
check text contains # tm status_TC_02 200
Case 2: SSL client validation
Suppose that you'd like to configure SSL with the following certificate authentications:
- Path to the keystore to use when locating client certificates:
C:/Test\_Folder/newkeystore.jks - The keystore password:
123456 - The trust store to use:
C:/Test\_Folder/cacerts - The trust store password:
changeit
Your JSON string should resemble as follows:
{"ssl":{"pathToKeyStore":"C:/Test_Folder/newkeystore.jks","keyStorePassword":"123456","pathToTrustStore":"C:/Test_Folder/cacerts","trustStorePassword":"changeit"}}
values
configure web service settings {"ssl":{"pathToKeyStore":"C:/Test_Folder/newkeystore.jks","keyStorePassword":"123456","pathToTrustStore":"C:/Test_Folder/cacerts","trustStorePassword":"changeit"}}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header content-type application/json
add http header Authorization # tm token
 
uri method variable
send http request # api test https GET _response_TC_03
 
response status
parse http reponse #_response_TC_03 tm status_TC_03
 
text fragment
check text contains # tm status_TC_03 200
Example: Cookies configuration
Suppose that you'd like to specify the following cookies which are sent to the server.
yummy\_cookie=chocotasty\_cookie=strawberry
Your JSON string should resemble as follows:
{"cookies":{"yummy_cookie":"choco","tasty_cookie":"strawberry"}}
values
configure web service settings {"cookies":{"yummy_cookie":"choco","tasty_cookie":"strawberry"}}
 
create http request
 
uri method variable
send http request # tm url POST tm_result
 
response status header body
parse http response # tm_result tm_status tm_header tm_body
 
text fragment
check text contains # tm status_TC_03 200
Example - Case 4: Encoder configuration
Suppose that you'd like to specify the following configurations for the encoder.
- The default charset to use for the specific content-type.
application/json=UTF-8text/plain=US-ASCII
- The default charset for query parameters.
defaultQueryParameterCharset=US-ASCII
- REST Assured does not encode the URL.
urlEncodingEnabled=false
JSON string resembles the following:
{"encoder":{"contentTypeToDefaultCharset":{"application/json":"UTF-8","text/plain":"US-ASCII"},"defaultQueryParameterCharset":"US-ASCII","urlEncodingEnabled":"false"}}
values
configure web service settings {"encoder":{"contentTypeToDefaultCharset":{"application/json":"UTF-8","text/plain":"US-ASCII"},"defaultQueryParameterCharset":"US-ASCII","urlEncodingEnabled":"false"}}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header path # tm path
 
content
add http body #tm text body content
 
uri method variable
send http request # tm encode url POST _response_TC_03_1
Example - Case 5: Decoder configuration
Suppose that you'd like to specify the following configurations for the decoder.
- The default charset to use for the specific content-type.
application/octet-stream=us-ascii
- The content decoder to apply: No compression.Notes:When you do this the Accept-Encoding header will be added automatically to the request and the response body will not be encoded. In this case, identity value, which indicates no compression, is enabled.
JSON string resembles the following:
{"decoder":{"contentDecoders":"identity","contentTypeToDefaultCharset":{"application/octet-stream":"us-ascii"}}}
values
configure web service settings {"decoder":{"contentDecoders":"identity","contentTypeToDefaultCharset":{"application/octet-stream":"us-ascii"}}}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header encoding deflate
add http header media_type #tm content type
add http header path # cf server attachment location & "\" & tm input
add http header output_path # cf server attachment location & "\" & tm output
add http header type deflate
 
uri method variable
send http request # api decoder GET tm result
 
response status header body
parse http response # tm result tm status tm header tm body
 
value expected
check value # tm status 200
Example - Case 6: Redirect configuration
Suppose that you'd like to configure the following redirect settings:
- Follow redirects.
followRedirects=true
- Allow circular redirects.
allowCircularRedirects=true
- Reject relative redirects.
rejectRelativeRedirect=true
- The maximum number of redirects: 50.
maxRedirects=50
JSON string resembles the following:
{"redirect":{"followRedirects":"true","allowCircularRedirects":"true","rejectRelativeRedirect":"true","maxRedirects":50}}
values
configure web service settings {"redirect":{"followRedirects":"true","allowCircularRedirects":"true","rejectRelativeRedirect":"true","maxRedirects":50}}
 
create http request
 
key value
add http header Content-Type application/json
 
uri method variable
send http request # ds url GET tm result
 
result description
report check # ds report check # ds expected 1
 
response status header body
parse http response # tm_result tm_status tm_header tm_body
 
value expected
check value #tm_status # ds status
- It is required that you declare configure web service settings with its configurations, before using the create http request built-in action.
- For a full list of web service's configurations, supported by TestArchitect, see "Supported web service's configurations" below.
- You may either declare various web service's configurations in a single configure web service settings action, or in multiple configure web service settings actions. Note that, when identical configurations are declared simultaneously, the latter configuration overrides the former one.
Supported web service's configurations
- Proxy: Defines a manual proxy server.Remember:To specify that the proxy is not in use, simply do not call configure web service settings with proxy settings in your test procedures.
- JSON string for manual proxy settings must be defined as follows.
{"proxy":{"hostname":"<value>","port":<value>,"scheme":"<value>","username":"<value>","password":"<value>"}}Key Description hostname - (Required) The proxy host to use. port - (Required) The proxy port to use. scheme - (Optional) The scheme of the proxy.
- When this key's value is empty, by default, the value of HTTP is used.
- Supported scheme(s):
HTTPRestriction:REST Assured, a Java framework for simplifying testing of REST based services built on top of HTTP Builder, and currently employed in TestArchitect, does not fully support HTTPS connection over proxy servers.username - (Optional) The username sent for proxy authentications.
- When this argument's key is empty, this key is ignored during automation.password - (Optional) The password sent for proxy authentications.
- When this argument's key is empty, this key is ignored during automation. - A sample JSON string might look like the following.
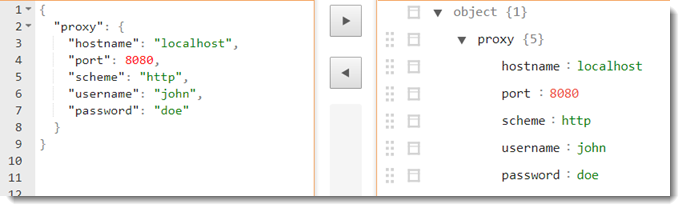
- To explicitly use system's proxy, apply the value of system for hostname and port.
{"proxy":{"hostname":"system","port":"system","scheme":"<value>","username":"<value>","password":"<value>"}}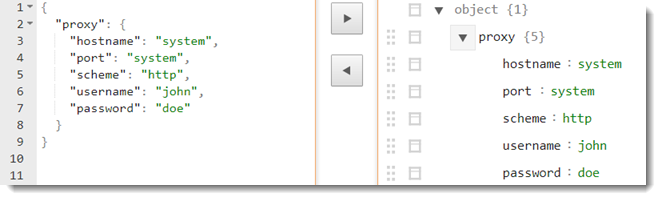 Note:
Note:- REST Assured automatically determines system proxy by looking at Java settings, environment variables, browser settings and operating system settings.
- TestArchitect supports mixed mode. Specially, you might use the system hostname in combination with a user-defined port, or vice versa.
- JSON string for manual proxy settings must be defined as follows.
- SSL: Defines SSL configurations. There are three supported modes in TestArchitect.
- Server validation: Run HTTPS normally, the SSL validation is handled from the server side.
- JSON string defined:
{"ssl":"trusted"}
- JSON string defined:
- No SSL validation: TestArchitect employs "relaxed HTTP validation", that is, skip SSL validation. Trust all hosts regardless if the SSL certificate is invalid. By using this mode, you don't need to specify a keystore or trust store.
- JSON string defined:
{"ssl":"skip"}
- JSON string defined:
- SSL client validation: You can be more fine-grained and have Java keystore file and use it with REST Assured.
- JSON string must be defined as follows.
{"ssl":{"pathToKeyStore":"<value>","pathToTrustStore":"<value>","keyStorePassword":"<value>","trustStorePassword":"<value>","port":<value>}}Option Description pathToKeyStore - (Required) The path to the keystore to use when locating client certificates. Remember:Please ensure that you have the keystore file beforehand. Otherwise, please follow this link, and read "Keystore Creation".
- Supported keystore types (learn more):
jceks: The proprietary keystore implementation provided by the SunJCE provider.
jks: The proprietary keystore implementation provided by the SUN provider.
pkcs12: The transfer syntax for personal identity information as defined in PKCS12.
- To separate directories in JSON, use four consecutive backslashes (\), or alternatively, use a single forward slash (/).keyStorePassword - (Optional) The password for the keystore. pathToTrustStore - (Optional) The path to trust store file.
- When this argument's key is empty, REST Assured automatically searches for a certificate file named cecarts, which resides in the security properties directory, java.home/lib/security, where java.home is the runtime environment's directory. (Learn more)
- To separate directories in JSON, use four consecutive backslashes (\), or alternatively, use a single forward slash (/).trustStorePassword - (Optional) The password for the trust store.
- When this argument's key is empty, this key is ignored during automation.port - (Optional) The port for SSL connections. Note:Most of the time you do not need to specify a port, since REST Assured will apply the configuration to the HTTPS port, defined in the URI.
- When this argument's key is empty, this key is ignored during automation. - A sample JSON string might look like the following.
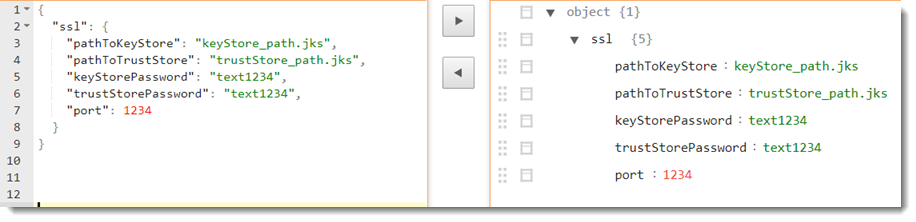
- JSON string must be defined as follows.
- Server validation: Run HTTPS normally, the SSL validation is handled from the server side.
- Cookies: Specifies HTTP cookies that are sent back to the server.
- JSON string for HTTP cookies must be defined as follows.
{"cookies":{"<cookie-name>":"<cookie-value1>","<cookie-name2>":"<cookie-value2>","<cookie-name3>":"<cookie-value3>"}}Note:A list of name-value pairs in the form of"<cookie-name>":"<cookie-value>". Pairs in the list are separated by a comma. - A sample JSON string might look like the following.
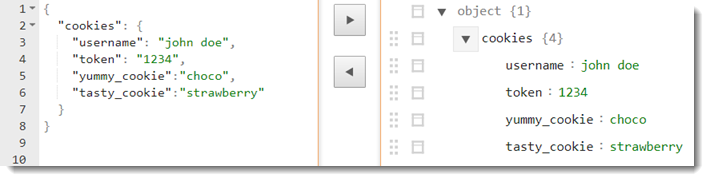
- JSON string for HTTP cookies must be defined as follows.
- Encoder: Specifies configurations for the encoder.
- JSON string for the encoder must be defined as follows.
{"encoder":{"contentTypeToDefaultCharset":{"<content-type1>":"<charset1>","<content-type2>":"<charset2>"},"defaultQueryParameterCharset":"<value>","defaultContentCharset":"<value>","urlEncodingEnabled": "<value>","addDefaultContentCharsetToContentType":"<value>"}}Option Description contentTypeToDefaultCharset - (Optional) Specify the default charset to use for the specific content-type.
- A list of pairs of the default charset to use for each specific content-type in the form of"<content-type>":"<charset>". Pairs in the list are separated by a comma.
- Supported keystore types (learn more):
- For a list of available content types, see here.
- For a list of available charsets, see here.
- When this argument's key is empty, this key is ignored during automation.defaultQueryParameterCharset - (Optional) Specify the default charset for query parameters.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of UTF-8 is used.
- If you don't want the query parameters to be encoded in the URL, it's highly recommended that you set urlEncodingEnabled to false.defaultContentCharset - (Optional) Specify the default charset for the body/content in the request specification.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of ISO-8859-1 is used.
- When contentTypeToDefaultCharset and defaultContentCharset are defined simultaneously, contentTypeToDefaultCharset has precedence.urlEncodingEnabled - (Optional) (Boolean value) Specify if URL is encoded automatically. Usually this is a recommended but in some cases, e.g. the query parameters are already be encoded before you provide them to REST Assured then it's useful to disable URL encoding. Specifically, the query is already URL encoded so you need to disable REST Assured's URL encoding to prevent double encoding.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of true is used.addDefaultContentCharsetToContentType - (Optional) (Boolean value) Tells whether REST Assured should automatically append the content charset to the content-type header if content charset is not defined explicitly.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of true is used. - A sample JSON string might look like the following.
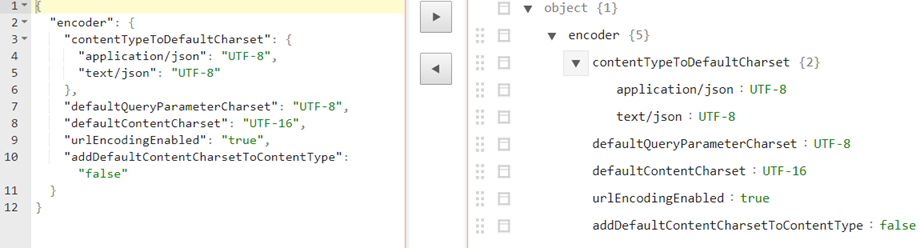
- JSON string for the encoder must be defined as follows.
- Decoder: Specifies configurations for the decoder.
- JSON string for the decoder must be defined as follows.
{"decoder":{"contentDecoders":"<value>","contentTypeToDefaultCharset":{"<content-type1>":"<charset1>","<content-type2>":"<charset2>"}}}Option Description contentDecoders - (Optional) Specify the content decoders that will be presented to the server when making a request (using the Accept-Encoding header). If the server supports any of these encodings then REST Assured will automatically perform decoding of the response accordingly.
- Supported modes:
1. default: (Default) In REST Assured, gzip and deflate are used.
- DecoderConfig.ContentDecoder.GZIP
- DecoderConfig.ContentDecoder.DEFLATE
2. identity: No compression (learn more).contentTypeToDefaultCharset - (Optional) Specify the default charset to use for the specific content-type.
- A list of pairs of the default charset to use for each specific content-type in the form of"<content-type>":"<charset>".
Pairs in the list are separated by a comma.
- For a list of available content types, see here.
- For a list of available charsets, see here.
- When this argument's key is empty, this key is ignored during automation. - A sample JSON string might look like the following.
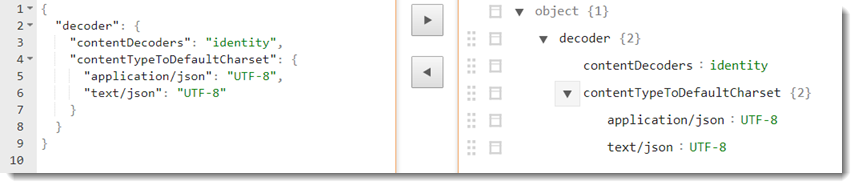
- JSON string for the decoder must be defined as follows.
- Redirect: Configures the redirect settings
- JSON string for the redirect must be defined as follows.
{"redirect":{"followRedirects":"<value>","allowCircularRedirects":"<value>","rejectRelativeRedirect":"<value>","maxRedirects":<value>}}Option Description followRedirects - (Optional) (Boolean value) Defines whether redirects should be handled automatically.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of true is used.allowCircularRedirects - (Optional) (Boolean value) Defines whether circular redirects (redirects to the same location) should be allowed.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of false is used.rejectRelativeRedirect - (Optional) (Boolean value) Defines whether relative redirects should be rejected. HTTP specification requires the location value be an absolute URI.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of false is used.maxRedirects - (Optional) (Boolean value) Defines the maximum number of redirects to be followed. The limit on number of redirects is intended to prevent infinite loops caused by broken server side scripts.
- When this argument's key is empty, by default, the value of 100 is used. - A sample JSON string might look like the following.
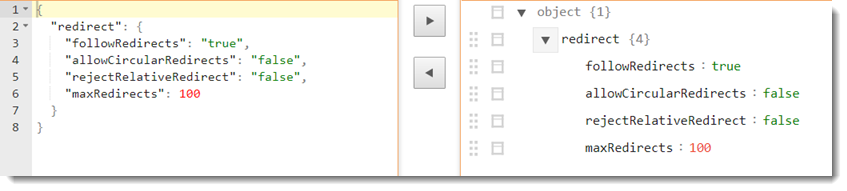
- JSON string for the redirect must be defined as follows.